Regions and Availability Zones (Again)
Hint: They're mandatory buddies.
Some Defaults Can’t Be Changed
As you get used to the concept of regions and availability zones and use them as the bedrock, so to speak, in your application stack design, it's important to remember that most infrastructure services offered by AWS operate as regional services operating across multiple availability zones.
Every EC2 instance deployed by a customer must be explicitly configured to launch in a specific availability zone. Other selected AWS services automatically distribute the required compute and storage resources across multiple availability zones to ensure the service's durability and availability.
AWS certification exams, such as the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate exam, heavily emphasize AZ-aware designs using knowledge of multi-AZ deployments.
Designing with multiple AZs prepares for real-world scenarios where downtime, performance, and cost are critical factors.
Every architect’s decision, from deploying custom EC2 instances with EBS volumes to deploying and managing relational databases such as RDS, must plan and affirm proper AZ placement to ensure resilience, performance, and cost efficiency.
Here’s a partial list of AWS services you need to know for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 exam.
Each listed service has at least one thing in common: They are deployed in availability zones within the selected AWS region.
What’s the purpose of each service, and what is the most common use case?
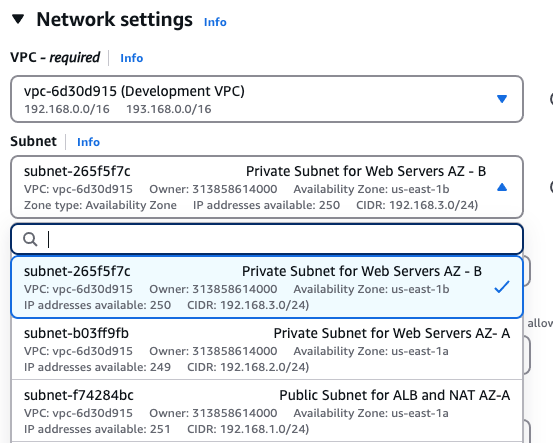
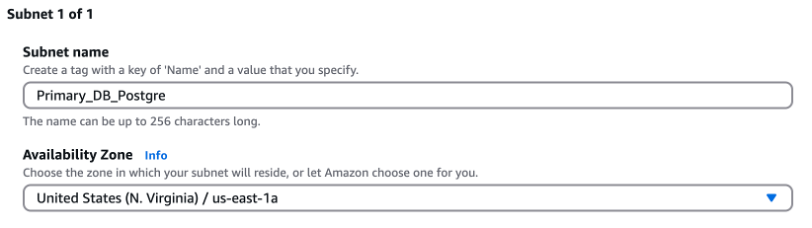
Amazon EC2: An EC2 instance must be launched on a subnet in a specific availability zone. You get to select the region and availability zone.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Supports multi-AZ deployments where one or more standby replicas are provisioned in different availability zones for high availability and failover support. Before installation, create a DB subnet group that is selected during database deployment, linking the databases to your VPC and subnets.
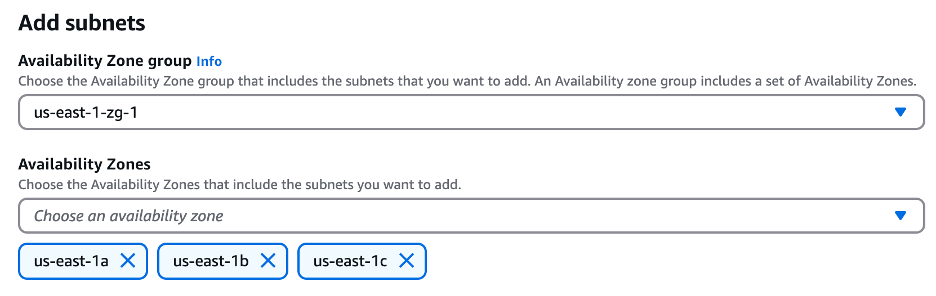
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service): Objects are automatically stored in a bucket across at least three availability zones within the selected region for durability and availability. AWS selects the number of availability zones used.
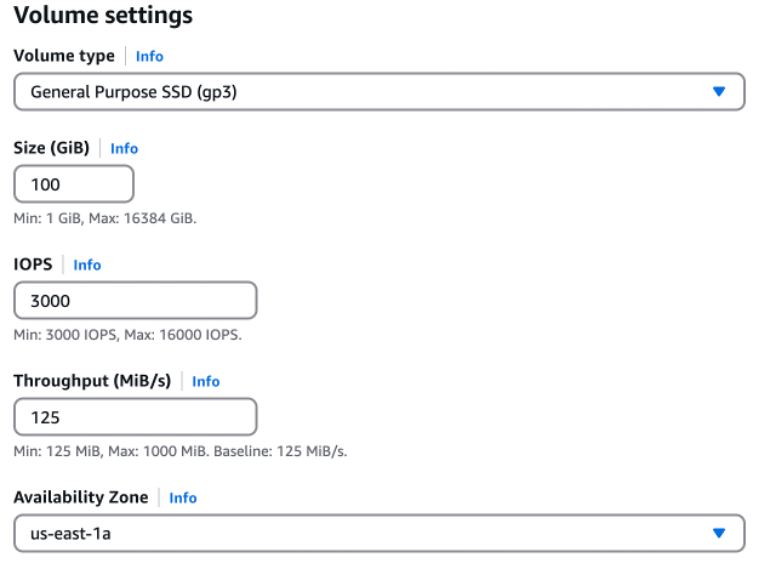
Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store): EBS volumes are tied to specific availability zones. EBS snapshots are stored in S3 and replicated across availability zones for additional safekeeping. The availability zone is selected during the creation of the EBS volume.
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Subnets are created within each VPC The availability zone for each subnet must be selected.
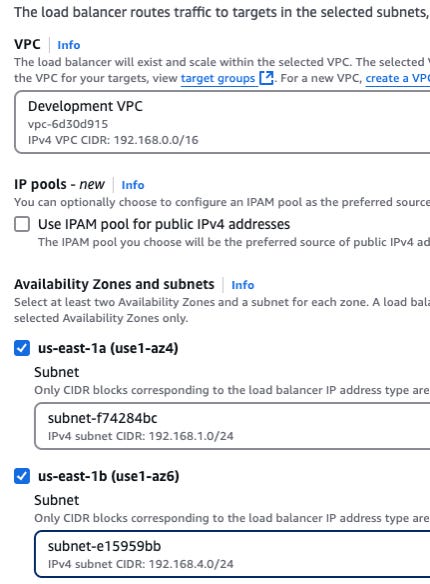
Elastic Load Balancing: Application Load Balancers distribute traffic across at least two availability zones within the selected VPC. The VPC availability zone and subnet must be selected.
There’s More!
The AWS services listed here are also defined as regional services typically deployed across at least two availability zones.
Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service): Deploy container instances across multiple availability zones within an ECS cluster.
Amazon DynamoDB: Automatically replicates data across three availability zones within the selected region for high availability and durability. DynamoDB can also be deployed globally across multiple regions.
Amazon Aurora: MySQL and PostgreSQL relational database deployments utilizing cluster-shared-storage arrays that replicate data across three availability zones. Aurora can also be deployed globally across multiple regions.
Amazon Redshift: Data warehouse clusters are deployed across multiple availability zones for enhanced high availability.
Amazon ElastiCache: This service supports multi-AZ deployments for in-memory caching (Redis and Memcached), ensuring high availability.
Amazon FSx for Windows File Server: Windows file system shares can be configured for multi-AZ deployments.
AWS Database Migration Service (DMS): To manage database migrations, replication instances can be launched in specific availability zones.
Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce): Big data processing clusters can be deployed across multiple availability zones.
AWS Lambda: A function-as-a-service computing service where the underlying infrastructure is spread across multiple availability zones for high availability.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): A regional messaging service designed to be highly available and operates across multiple availability zones.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): A regional notification service that leverages multiple availability zones for reliability.
AWS Step Functions: A regional workflow orchestration service operating with high availability across availability zones.
Exam Prep Tips:
To help prepare for the exam, use the AWS FAQS to start building your own cheat sheet. AWS FAQs
Write a two-sentence blurb describing the purpose of each service and a use case of each of the above services.
Writing concise technical information in your own words will be remembered when test time arrives.